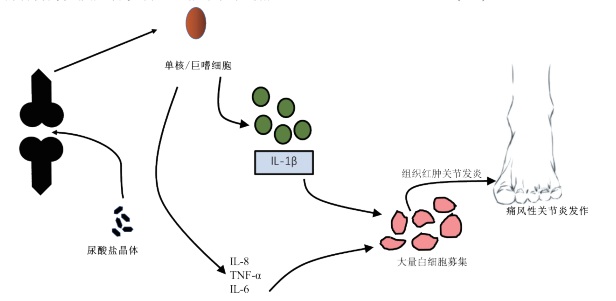
Gouty arthritis (GA) is an acute inflammatory that is initiated by the precipitation of oversaturated solutions of uric acid as
monosodium urate (MSU) crystals, which activates neutrophils to release neutrophil extracellular traps (NETs). NETs further enhance
the inflammatory response by inducing neutrophils and monocytes to release pro-inflammatory cytokines and chemokines. However,
the increasing number of neutrophils recruited to the sites of MSU deposits allows the formation of aggregated NETs that densely
packs MSU crystals and degrades the proinflammatory cytokines, thereby allowing turning down the inflammatory. Here we briefly
summarize the dual role of neutrophils during the initiation, development and the resolution of GA, and the signal pathways involved
in the regulation of NETs formation.
WANG Xuelin, CAO Xiumei, YAN Jianshe
. The role of neutrophil extracellular traps in gouty arthritis: two sides of the same
coin[J]. Chinese Journal of Nature, 2021
, 43(2)
: 135
-140
.
DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.0253-9608.2021.02.008