

Assembly and promoter recognition mechanisms of pretranscriptional initiation complexes
Received date: 2022-12-19
Online published: 2023-03-29
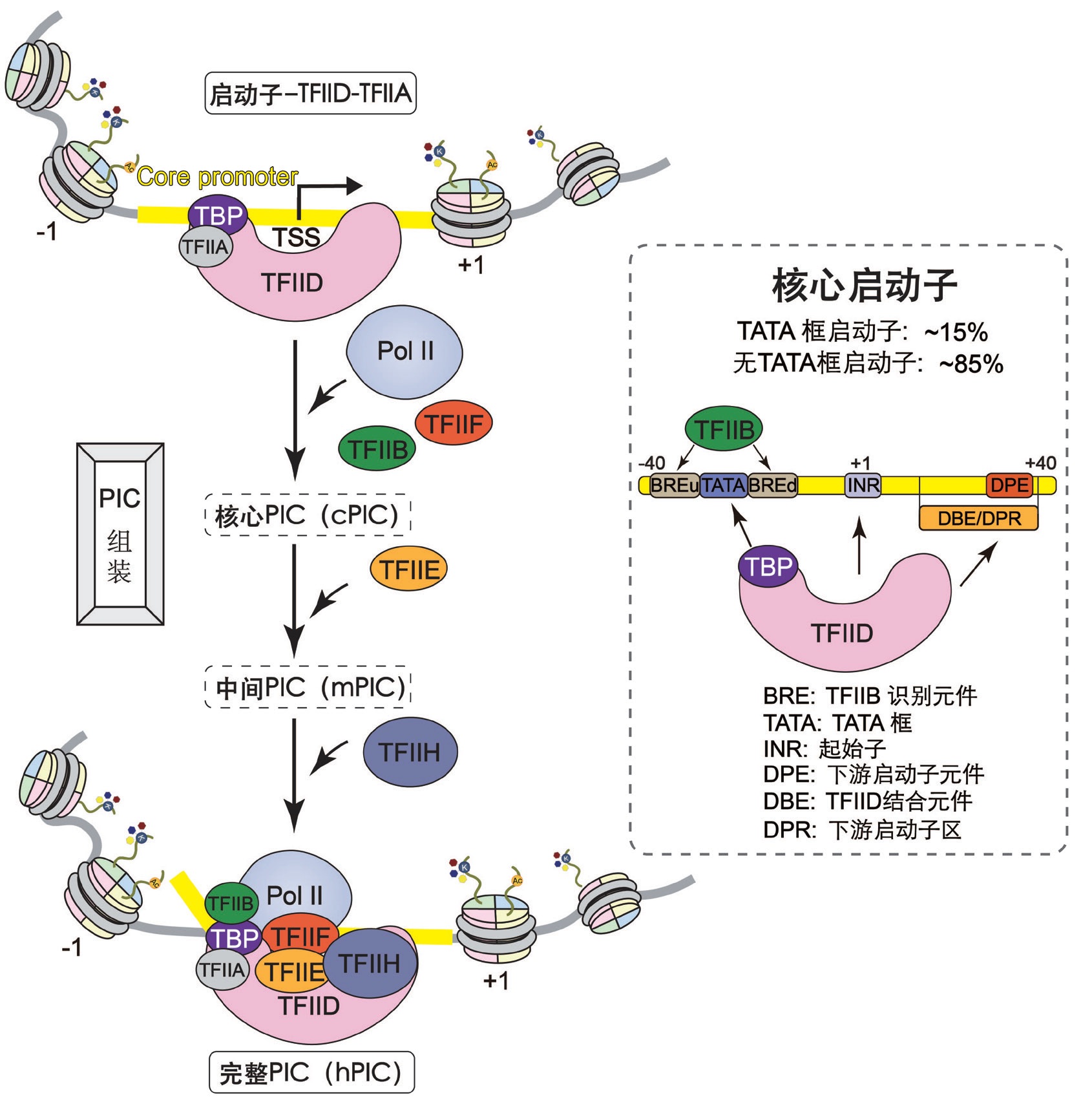
CHEN Xizi, XU Yanhui . Assembly and promoter recognition mechanisms of pretranscriptional initiation complexes[J]. Chinese Journal of Nature, 2023 , 45(2) : 79 -88 . DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.0253-9608.2023.02.001
[4] WEIL P A, BLATTI S P. HeLa cell deoxyribonucleic acid dependent RNA polymerases: function and properties of the class III enzymes [J]. Biochemistry, 1976, 15(7): 1500-1509.
[5] JUVEN-GERSHON T, KADONAGA J T. Regulation of gene expression via the core promoter and the basal transcriptional
machinery [J]. Dev Biol, 2010, 339(2): 225-229.
[6] VO NGOC L, WANG Y L, KASSAVETIS G A, et al. The punctilious RNA polymerase II core promoter [J]. Genes Dev, 2017,
31(13): 1289-1301.
[7] SANDELIN A, CARNINCI P, LENHARD B, et al. Mammalian RNA polymerase II core promoters: insights from genome-wide
studies [J]. Nat Rev Genet, 2007, 8(6): 424-436.
[8] VO NGOC L, HUANG C Y, CASSIDY C J, et al. Identification of the human DPR core promoter element using machine learning [J]. Nature, 2020, 585(7825): 459-463.
[9] THOMAS M C, CHIANG C M. The general transcription machinery and general cofactors [J]. Crit Rev Biochem Mol Biol,
2006, 41(3): 105-178.
[10] BURATOWSKI S, HAHN S, GUARENTE L, et al. Five intermediate complexes in transcription initiation by RNA polymerase II [J]. Cell, 1989, 56(4): 549-561.
[11] VAN DYKE M W, ROEDER R G, SAWADOGO M. Physical analysis of transcription preinitiation complex assembly on a class II
gene promoter [J]. Science, 1988, 241(4871): 1335-1338.
[12] ZAWEL L, REINBERG D. Initiation of transcription by RNA polymerase II: a multi-step process [J]. Prog Nucleic Acid Res Mol
Biol, 1993, 44: 67-108.
[13] CHEN X, QI Y, WU Z, et al. Structural insights into preinitiation complex assembly on core promoters [J]. Science, 2021, 372(6541): eaba8490.
[14] BAEK I, FRIEDMAN L J, GELLES J, et al. Single-molecule studies reveal branched pathways for activator-dependent assembly
of RNA polymerase II pre-initiation complexes [J]. Mol Cell, 2021, 81(17): 3576-3588.e6.
[15] NGUYEN V Q, RANJAN A, LIU S, et al. Spatiotemporal coordination of transcription preinitiation complex assembly in live
cells [J]. Mol Cell, 2021, 81(17): 3560-3575.e6.
[16] ZHANG Z, ENGLISH B P, GRIMM J B, et al. Rapid dynamics of general transcription factor TFIIB binding during preinitiation
complex assembly revealed by single-molecule analysis [J]. Genes Dev, 2016, 30(18): 2106-2118.
[17] SVEJSTRUP J Q, WANG Z, FEAVE W J, et al. Different forms of TFIIH for transcription and DNA repair: holo-TFIIH and a
nucleotide excision repairosome [J]. Cell, 1995, 80(1): 21-28.
[18] SOUTOURINA J. Transcription regulation by the Mediator complex [J]. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol, 2018, 19(4): 262-274.
[19] PETERSON M G, TANESE N, PUGH B F, et al. Functional domains and upstream activation properties of cloned human TATA
binding protein [J]. Science, 1990, 248(4963): 1625-1630.
[20] VERRIJZER C P, CHEN J-L, YOKOMORI K, et al. Binding of TAFs to core elements directs promoter selectivity by RNA polymerase II [J]. Cell, 1995, 81(7): 1115-1125.
[21] NOGALES E, LOUDER R K, HE Y. Structural insights into the eukaryotic transcription initiation machinery [J]. Annu Rev Biophys, 2017, 46: 59-83.
[22] DONCZEW R, HAHN S. Mechanistic differences in transcription initiation at TATA-less and TATA-containing promoters [J]. Mol
Cell Biol, 2018, 38(1): e00448-17.
[23] DONCZEW R, WARFIELD L, PACHECO D, et al. Two roles for the yeast transcription coactivator SAGA and a set of genes redundantly regulated by TFIID and SAGA [J]. eLife, 2020, 9: e50109.
[24] TAATJES D J. The continuing SAGA of TFIID and RNA polymerase II transcription [J]. Mol Cell, 2017, 68(1): 1-2.
[25] NIKOLOV D B, CHEN H, HALAY E D, et al. Crystal structure of a TFIIB-TBP-TATA-element ternary complex [J]. Nature, 1995,
377(6545): 119-128.
[26] ZHAO X, HERR W. A regulated two-step mechanism of TBP binding to DNA: a solvent-exposed surface of TBP inhibits TATA
box recognition [J]. Cell, 2002, 108(5): 615-627.
[27] PATEL A B, LOUDER R K, GREBER B J, et al. Structure of human TFIID and mechanism of TBP loading onto promoter DNA [J].
Science, 2018, 362(6421): aau8872.
[28] LOUDER R K, HE Y, LÓPEZ-BLANCO J R, et al. Structure of promoter-bound TFIID and model of human pre-initiation complex
assembly [J]. Nature, 2016, 531(7596): 604-609.
[29] CIANFROCCO M A, KASSAVETIS G A, GROB P, et al. Human TFIID binds to core promoter DNA in a reorganized structural state [J]. Cell, 2013, 152(1/2): 120-131.
[30] KOLESNIKOVA O, BEN-SHEM A, LUO J, et al. Molecular structure of promoter-bound yeast TFIID [J]. Nat Commun, 2018,
9(1): 4666.
[31] JUVEN-GERSHON T, CHENG S, KADONAGA J T. Rational design of a super core promoter that enhances gene expression [J].
Nat Methods, 2006, 3(11): 917-922.
[32] LIU X, BUSHNELL D A, WANG D, et al. Structure of an RNA polymerase II-TFIIB complex and the transcription initiation
mechanism [J]. Science, 2010, 327(5962): 206-209.
[33] KOSTREWA D, ZELLER M E, ARMACHE K-J, et al. RNA polymerase II-TFIIB structure and mechanism of transcription initiation [J]. Nature, 2009, 462(7271): 323-330.
[34] ROBINSON P J, TRNKA M J, BUSHNELL D A, et al. Structure of a complete Mediator-RNA polymerase II pre-initiation complex [J]. Cell, 2016, 166(6): 1411-1422. e16.
[35] PLASCHKA C, HANTSCHE M, DIENEMANN C, et al. Transcription initiation complex structures elucidate DNA opening [J]. Nature, 2016, 533(7603): 353-358.
[36] HE Y, YAN C, FANG J, et al. Near-atomic resolution visualization of human transcription promoter opening [J]. Nature, 2016,
533(7603): 359-365.
[37] PLASCHKA C, LARIVIÈRE L, WENZECK L, et al. Architecture of the RNA polymerase II-Mediator core initiation complex [J].
Nature, 2015, 518(7539): 376-380.
[38] MURAKAMI K, TSAI K-L, KALISMAN N, et al. Structure of an RNA polymerase II preinitiation complex [J]. Proc Natl Acad Sci
USA, 2015, 112(44): 13543-13548.
[39] MURAKAMI K, ELMLUND H, KALISMAN N, et al. Architecture of an RNA polymerase II transcription pre-initiation complex [J].
Science, 2013, 342(6159): 1238724.
[40] HE Y, FANG J, TAATJES D J, et al. Structural visualization of key steps in human transcription initiation [J]. Nature, 2013, 495(7442): 481-486.
[41] SCHILBACH S, AIBARA S, DIENEMANN C, et al. Structure of RNA polymerase II pre-initiation complex at 2.9 Å defines initial
DNA opening [J]. Cell, 2021, 184(15): 4064-4072. e28.
[42] AIBARA S, SCHILBACH S, CRAMER P. Structures of mammalian RNA polymerase II pre-initiation complexes [J]. Nature, 2021,
594(7861): 124-128.
[43] YANG C, FUJIWARA R, KIM H J, et al. Structural visualization of de novo transcription initiation by Saccharomyces cerevisiae RNA polymerase II [J]. Mol Cell, 2022, 82: 660-676. e9.
[44] RENGACHARI S, SCHILBACH S, AIBARA S, et al. Structure of the human Mediator-RNA polymerase II pre-initiation complex [J]. Nature, 2021, 594(7861): 129-133.
[45] ABDELLA R, TALYZINA A, CHEN S, et al. Structure of the human Mediator-bound transcription preinitiation complex [J].
Science, 2021, 372(6537): 52-56.
[46] SCHILBACH S, HANTSCHE M, TEGUNOV D, et al. Structures of transcription pre-initiation complex with TFIIH and Mediator [J]. Nature, 2017, 551(7679): 204-209.
[47] GRUNBERG S, WARFIELD L, HAHN S. Architecture of the RNA polymerase II preinitiation complex and mechanism of ATPdependent promoter opening [J]. Nat Struct Mol Biol, 2012, 19(8): 788-796.
[48] CHEN X, QI Y, WU Z, et al. Structural insights into preinitiation complex assembly on core promoters [J]. Science, 2021, 372(6541): eaba8490.
[49] CHEN X, YIN X, LI J, et al. Structures of the human Mediator and Mediator-bound preinitiation complex [J]. Science, 2021,
372(6546): eabg0635.
[50] HABERLE V, STARK A. Eukaryotic core promoters and the functional basis of transcription initiation [J]. Nat Rev Mol Cell
Biol, 2018, 19(10): 621-637.
[51] WEBER C M, RAMACHANDRAN S, HENIKOFF S. Nucleosomes are context-specific, H2A.Z-modulated barriers to RNA polymerase [J]. Mol Cell, 2014, 53(5): 819-830.
[52] TEVES S S, WEBER C M, HENIKOFF S. Transcribing through the nucleosome [J]. Trends Biochem Sci, 2014, 39(12): 577-586.
[53] LAI W K M, PUGH B F. Understanding nucleosome dynamics and their links to gene expression and DNA replication [J]. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol, 2017, 18(9): 548-562.
[54] JIANG C, PUGH B F. Nucleosome positioning and gene regulation: advances through genomics [J]. Nat Rev Genet, 2009, 10(3): 161-172.
[55] KORNBERG R D, LORCH Y. Primary role of the nucleosome [J]. Mol Cell, 2020, 79(3): 371-375.
[56] STRUHL K, SEGAL E. Determinants of nucleosome positioning [J]. Nat Struct Mol Biol, 2013, 20(3): 267-273.
[57] JIN C, ZANG C, WEI G, et al. H3.3/H2A.Z double variantcontaining nucleosomes mark ‘nucleosome-free regions’ of active
promoters and other regulatory regions [J]. Nat Genet, 2009, 41(8): 941-945.
[58] RHEE H S, BATAILLE A R, ZHANG L, et al. Subnucleosomal structures and nucleosome asymmetry across a genome [J]. Cell,
2014, 159(6): 1377-1388.
[59] SCHONES D E, CUI K, CUDDAPAH S, et al. Dynamic regulation of nucleosome positioning in the human genome [J]. Cell, 2008, 132(5): 887-898.
[60] MAVRICH T N, JIANG C, IOSHIKHES I P, et al. Nucleosome organization in the Drosophila genome [J]. Nature, 2008, 453(7193): 358-362.
[61] TRAMANTANO M, SUN L, AU C, et al. Constitutive turnover of histone H2A.Z at yeast promoters requires the preinitiation complex [J]. eLife, 2016, 5: e14243.
/
| 〈 |
|
〉 |