Thunderstorms and lightning are serious natural weather hazards that affect all areas of society and economy. Charge
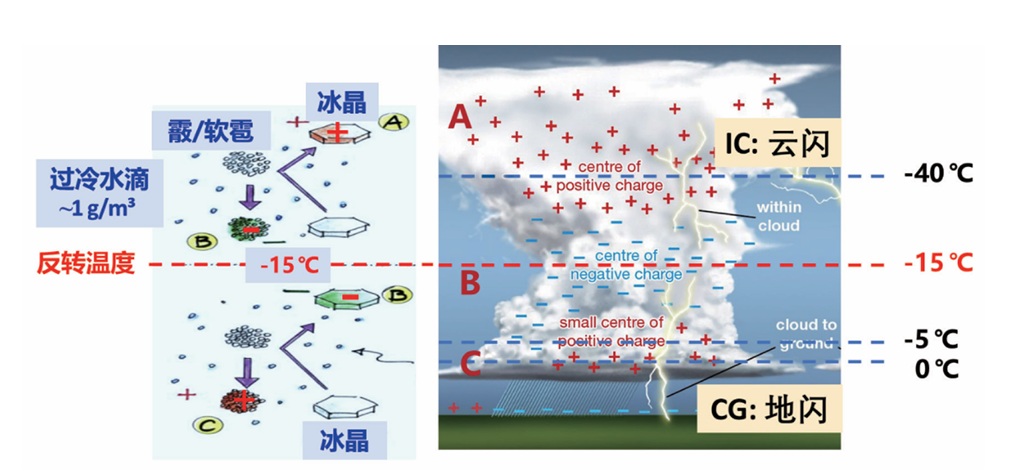
transfer between hydrometeors such as graupel and ice crystals occurs under the complex influence of cloud dynamics and
microphysical processes. This leads to the electrification of thunderstorms, which accumulate large amounts of charge in different
regions of the cloud, resulting in lightning discharges. Lightning can produce nitrogen oxides, high-energy radiation, and cause
material-energy exchanges in the upper and lower atmosphere, and the problems involved are multidisciplinary. The Tibetan Plateau
is characterized by high altitude, large and complex topography, with frequent thunderstorms and lightning activity. Research by
Chinese scientists has revealed its bottom-heavy tripolar charge structure with a strong lower positive charge center, which generally
evolves from an initial inverted dipole. Its universality has been confirmed by studies of thunderstorms in other high-altitude regions.
The unique structure of thunderstorms on the Tibetan Plateau and their responses and feedbacks to global and regional ecosystems
and climate change, which are controlled by a combination of large-scale circulation and local thermodynamic factors, deserve further
attention and focus. Triggering lightning technology allows the highly random lightning to occur in a certain spatial and temporal
controlled state, providing unique conditions for research into the physical mechanisms and effects of lightning, as well as for testing
of lightning protection technology, based on which a series of advances have been achieved. In the future, the artificial intervention
of thunderstorms and lightning by influencing the process of cloud electrification and triggering lightning at high altitude is still to be
explored through the development of a variety of new technologies.
JIANG Rubin, LIU Dongxia, YUAN Shanfeng, ZHANG Hongbo, WU Xueke
. Thunderstorm electricity and rocket triggering lightning[J]. Chinese Journal of Nature, 2025
, 47(4)
: 249
-260
.
DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.0253-9608.2025.04.002


