

人源大麻素受体的结构生物学研究
Structural studies of human cannabinoid receptors
Received date: 2020-10-01
Online published: 2021-02-25
沈灵, 华甜, 刘志杰 . 人源大麻素受体的结构生物学研究[J]. 自然杂志, 2021 , 43(1) : 25 -31 . DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.0253-9608.2021.01.004

[1] PERTWEE R G. Cannabinoid pharmacology: the first 66 years [J]. Br J Pharmacol, 2006, 147(S1): S163-171.
[2] GAONI Y, MECHOULAM R. Isolation, structure, and partial synthesis of an active constituent of hashish [J]. J Am Chem Soc, 1964, 86(8): 1646-1647.
[3] AVICO U, PACIFICI R, ZUCCARO P. Variations of tetrahydrocannabinol content in cannabis plants to distinguish the fibre-type from drug-type plants [J]. Bull Narc, 1985, 37: 61-65.
[4] XU S W, LIU H. Promising prospect of developing industrial hemp [J]. China Textile Leader, 2005, 8: 22-26.
[5] LEMBERGER L. Potential therapeutic usefulness of marijuana [J]. Annu Rev Pharmacol Toxicol, 1980, 20: 151-172.
[6] ADAMS R, HUNT M, CLARK J H. Structure of cannabidiol, a product isolated from the marihuana extract of minnesota wild hemp [J]. J Chem Soc, 1940, 62: 196-200.
[7] JACOB A, TODD A R. Cannabis indica. Part II. Isolation of cannabidiol from Egyptian hashish. Observations on the structure of cannabinol [J]. J Chem Soc, 1940: 649-653.
[8] DEVANE W A, HANUS L, BREUER A, et al. Isolation and structure of a brain constituent that binds to the cannabinoid receptor [J]. Science, 1992, 258: 1946-1949.
[9] FORD B M, TAI S, FANTEGROSSI W E, et al. Synthetic pot: Not your grandfather’s marijuana [J]. Trends Pharmacol Sci, 2017, 38: 257-276.
[10] PACHER P, KUNOS G. Modulating the endocannabinoid system in human health and disease — successes and failures [J]. FEBS J, 2013, 280: 1918-1943.
[11] GLEASON K A, BIRNBAUM S G, SHUKLA A, et al. Susceptibility of the adolescent brain to cannabinoids: long-term
hippocampal effects and relevance to schizophrenia [J]. Transl Psychiatry, 2012, 2: e199.
[12] AIZPURUA-OLAIZOLA O, ELEZGARAI I, RICO-BARRIO I, et al. Targeting the endocannabinoid system: future therapeutic strategies [J]. Drug Discov Today, 2017, 22: 105-110.
[13] HOWLETT A C, BARTH F, BONNER T I, et al. International union of pharmacology. XXVII. Classification of cannabinoid receptors [J]. Pharmacol Rev, 2002, 54: 161-202.
[14] HERKENHAM M, LYNN A B, LITTLE M D, et al. Cannabinoid receptor localization in brain [J]. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA, 1990, 87: 1932-1936.
[15] MUNRO S, THOMAS K L, ABU-SHAAR M. Molecular characterization of a peripheral receptor for cannabinoids [J]. Nature, 1993, 365: 61-65.
[16] MALLIPEDDI S, JANERO D R, ZVONOK N, et al. Functional selectivity at G-protein coupled receptors: Advancing cannabinoid receptors as drug targets [J]. Biochem Pharmacol, 2017, 128: 1-11.
[17] GLASS M, FELDER C C. Concurrent stimulation of cannabinoid CB1 and dopamine D2 receptors augments cAMP accumulation in striatal neurons: evidence for a Gs linkage to the CB1 receptor [J]. J Neurosci, 1997, 17: 5327-5333.
[18] LAUCKNER J E, HILLE B, MACKIE K. The cannabinoid agonist WIN55,212-2 increases intracellular calcium via CB1 receptor coupling to Gq/11 G proteins [J]. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA, 2005, 102: 19144-19149.
[19] DONVITO G, NASS S R, WILKERSON J L, et al. The endogenous cannabinoid system: a budding source of targets for treating inflammatory and neuropathic pain [J]. Neuropsychopharmacology, 2018, 43: 52-79.
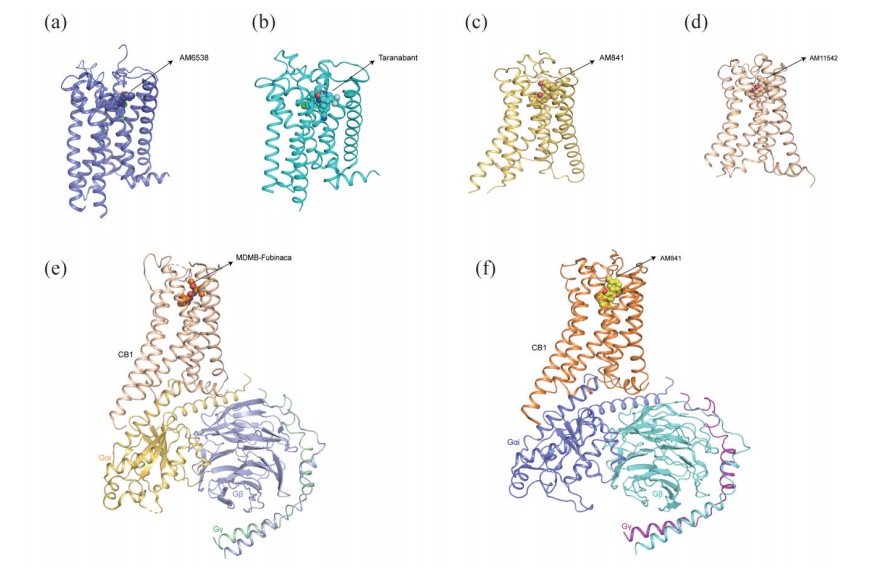
[20] HUA T, VEMURI K, PU M, et al. Crystal structure of the human cannabinoid receptor CB1 [J]. Cell, 2016, 167: 750-762. e14.
[21] SHAO Z, YIN J, CHAPMAN K, et al. High-resolution crystal structure of the human CB1 cannabinoid receptor [J]. Nature, 2016, 540: 602-606.
[22] HURST D P, SCHMEISSER M, REGGIO P H. Endogenous lipid activated G protein-coupled receptors: emerging structural features from crystallography and molecular dynamics simulations [J]. Chem Phys Lipids, 2013, 169: 46-56.
[23] SIM-SELLEY L J, GOFORTH P B, MBA M U, et al. Sphingosine-1- phosphate receptors mediate neuromodulatory functions in the CNS [J]. J Neurochem, 2009, 110: 1191-1202.
[24] DE SAN ROMAN E G, MANUEL I, LEDENT C, et al. CB1 and LPA1 receptors relationship in the mouse central nervous system [J]. Front Mol Neurosci, 2019, 12: 223.
[25] FAY J F, DUNHAM T D, FARRENS D L. Cysteine residues in the human cannabinoid receptor: only C257 and C264 are required for a functional receptor, and steric bulk at C386 impairs antagonist SR141716A binding [J]. Biochemistry, 2005, 44: 8757-8769.
[26] HUA T, VEMURI K, NIKAS S P, et al. Crystal structures of agonistbound human cannabinoid receptor CB1 [J]. Nature, 2017, 547: 468-471.
[27] KRISHNA KUMAR K, SHALEV-BENAMI M, ROBERTSON M J, et al. Structure of a signaling cannabinoid receptor 1-G protein complex [J]. Cell, 2019, 176: 448-458. e12.
[28] HUA T, LI X, WU L, et al. Activation and signaling mechanism revealed by cannabinoid receptor-Gi complex structures [J]. Cell, 2020, 180(4): 655-665. e18.
[29] LI X, HUA T, VEMURI K, et al. Crystal structure of the human cannabinoid receptor CB2 [J]. Cell, 2019, 176: 459-467. e13.
[30] LUNN C A, REICH E P, FINE J S, et al. Biology and therapeutic potential of cannabinoid CB2 receptor inverse agonists [J]. Br J Pharmacol, 2008, 153: 226-239.
[31] CONTINO M, CAPPARELLI E, COLABUFO N A, et al. Editorial: The CB2 cannabinoid system: A new strategy in neurodegenerative disorder and neuroinflammation [J]. Front Neurosci, 2017, 11: 196. doi: 10.3389/fnins.2017.00196.
[32] XING C, ZHUANG Y, XU T H, et al. Cryo-EM structure of the human cannabinoid receptor CB2-Gi signaling complex [J]. Cell, 2020, 180: 645-654. e13.
/
| 〈 |
|
〉 |