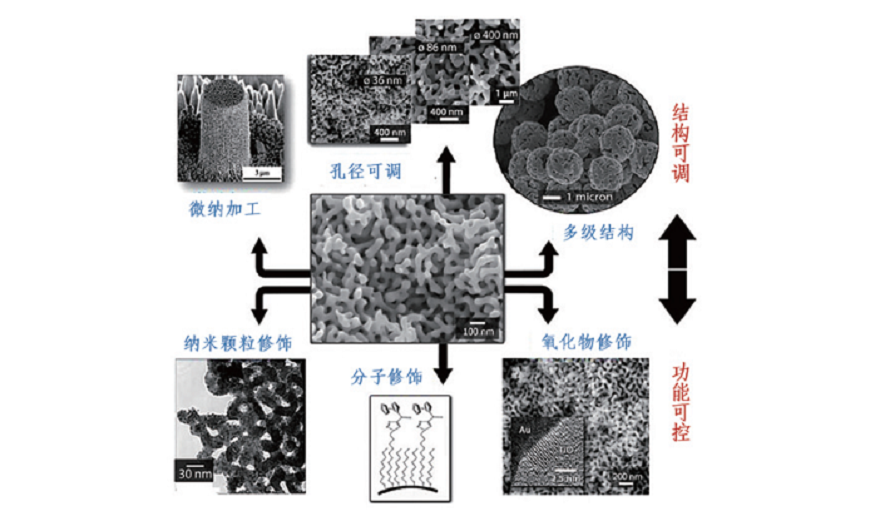
纳米多孔金属是一类具有三维孔隙/韧带双连通结构的材料,具备高比表面积、化学稳定、特征结构稳定可调控、可选材料体系众多等特点,已成为电化学催化、储能领域的研究热点。近年来,基于其微纳尺度特征尺寸及金属特有的表面等离激元效应,纳米多孔金属已展现出在传感及检测应用领域的巨大潜力。文章讨论了纳米多孔金属的各类制备方法的优缺点,并简要介绍了金属表面等离激元材料及其在检测、致动、传感领域的典型应用。
Nanoporous metals (NPMs) are metals/alloys with a characteristic bicontinuous structure of three-dimensional and nano-sized pores/ligaments. In recent years, NPMs have attracted numerous scientific and technological interests in fields such as electrochemical catalysis and energy storage owing to their high specific areas, desirable chemicasl stability, stable and tunable geometric structure and a diversity of candidate materials. Moreover, NPMs have been considered as a promising candidate with great potentials in applications of sensing and trace detection for their unique surface plasmonic properties originating from submicron scale characteristic dimension of metallic compounds. This article reviews the recent advances in synthesis methods of nanoporous metals as well as their respective advantages and limitations, followed by typical applications of NPMs in detection, actuation and sensing.