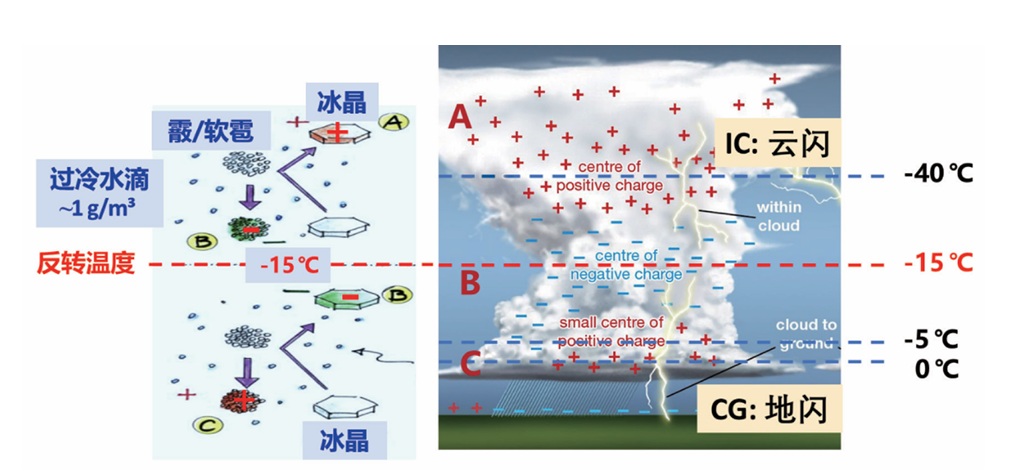
雷暴和闪电是严重的自然天气灾害,影响社会经济各个领域。云动力和微物理过程的共同作用,使电荷在霰、冰晶等
水成物粒子之间转移。这导致雷暴云带电,并在不同区域聚集大量电荷,从而发生闪电放电。闪电可产生氮氧化物、高能辐射,引起上下大气层物质和能量交换等,所涉及的问题是多学科的。青藏高原的特征是海拔高、面积大且地形复杂,雷暴和闪电活动频繁。中国科学家的研究揭示了青藏高原雷暴的下部主导型三级电荷分布模态,其普适性也被其他高海拔雷暴研究所证实。青藏高原雷暴的独特结构及其对全球和区域的生态环境及气候变化的响应与反馈,会受大尺度环流和局地热动力因素的共同控制,值得进一步关注和重视。人工引雷技术使随机性很高的闪电能够在一定时空可控的状态下发生,为闪电的物理机制和效应、雷击防护技术测试等研究提供了良好条件,基于此取得了一系列进展。未来,通过开发新技术来影响雷暴云起电过程或高空一定区域引发闪电以实现对雷暴、闪电的人工干预,仍有待深入探索。
Thunderstorms and lightning are serious natural weather hazards that affect all areas of society and economy. Charge
transfer between hydrometeors such as graupel and ice crystals occurs under the complex influence of cloud dynamics and
microphysical processes. This leads to the electrification of thunderstorms, which accumulate large amounts of charge in different
regions of the cloud, resulting in lightning discharges. Lightning can produce nitrogen oxides, high-energy radiation, and cause
material-energy exchanges in the upper and lower atmosphere, and the problems involved are multidisciplinary. The Tibetan Plateau
is characterized by high altitude, large and complex topography, with frequent thunderstorms and lightning activity. Research by
Chinese scientists has revealed its bottom-heavy tripolar charge structure with a strong lower positive charge center, which generally
evolves from an initial inverted dipole. Its universality has been confirmed by studies of thunderstorms in other high-altitude regions.
The unique structure of thunderstorms on the Tibetan Plateau and their responses and feedbacks to global and regional ecosystems
and climate change, which are controlled by a combination of large-scale circulation and local thermodynamic factors, deserve further
attention and focus. Triggering lightning technology allows the highly random lightning to occur in a certain spatial and temporal
controlled state, providing unique conditions for research into the physical mechanisms and effects of lightning, as well as for testing
of lightning protection technology, based on which a series of advances have been achieved. In the future, the artificial intervention
of thunderstorms and lightning by influencing the process of cloud electrification and triggering lightning at high altitude is still to be
explored through the development of a variety of new technologies.