

趋化因子受体的结构与信号转导机制
Structural and signaling mechanism of chemokine receptors
Received date: 2021-10-01
Online published: 2021-02-25
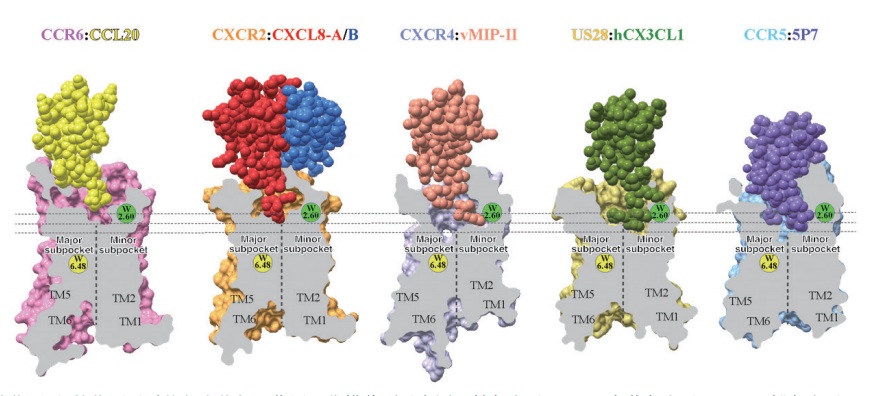
刘凯雯, 刘志杰, 华甜 . 趋化因子受体的结构与信号转导机制[J]. 自然杂志, 2021 , 43(1) : 18 -24 . DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.0253-9608.2021.01.003

[1] PIERCE K L, PREMONT R T, LEFKOWITZ R J. Seventransmembrane receptors [J]. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol, 2002, 3(9): 639-650. [2] HAUSER A S, ATTWOOD M M, RASK-ANDERSEN M, et al. Trends in GPCR drug discovery: new agents, targets and indications [J]. Nat Rev Drug Discov, 2017, 16(12): 829-842.
[3] MANTOVANI A, SAVINO B, LOCATI M, et al. The chemokine system in cancer biology and therapy [J]. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev, 2010, 21(1): 27-39.
[4] LE Y, ZHOU Y, IRIBARREN P, et al. Chemokines and chemokine receptors: their manifold roles in homeostasis and disease [J]. Cell Mol Immunol, 2004, 1(2): 95-104.
[5] BIZZARRI C, BECCARI A R, BERTINI R, et al. ELR+ CXC chemokines and their receptors (CXC chemokine receptor 1 and CXC chemokine receptor 2) as new therapeutic targets [J]. Pharmacol Ther, 2006, 112(1): 139-149.
[6] ROLLINS B J. Chemokines [J]. Blood, 1997, 90(3): 909-928.
[7] BAGGIOLINI M. Chemokines and leukocyte traffic [J]. Nature, 1998, 392(6676): 565-568.
[8] GUO F, LONG L, WANG J, et al. Insights on CXC chemokine receptor 2 in breast cancer: An emerging target for oncotherapy [J]. Oncol Lett, 2019, 18(6): 5699-5708.
[9] QIN L, KUFAREVA I, HOLDEN LG, et al. Structural biology. Crystal structure of the chemokine receptor CXCR4 in complex with a viral chemokine [J]. Science, 2015, 347(6226): 1117-1122.
[10] BURG J S, INGRAM J R, VENKATAKRISHNAN A J, et al. Structural biology. Structural basis for chemokine recognition and activation of a viral G protein-coupled receptor [J]. Science, 2015, 347(6226): 1113-1117.
[11] ZHENG Y, HAN G W, ABAGYAN R, et al. Structure of CC chemokine receptor 5 with a potent chemokine antagonist reveals mechanisms of chemokine recognition and molecular mimicry by HIV [J]. Immunity, 2017, 46(6): 1005-1017. e5.
[12] WASILKO D J, JOHNSON Z L, AMMIRATI M, et al. Structural basis for chemokine receptor CCR6 activation by the endogenous protein ligand CCL20 [J]. Nat Commun, 2020, 11(1): 3031.
[13] LIU K, WU L, YUAN S, et al. Structural basis of CXC chemokine receptor 2 activation and signalling [J]. Nature, 2020, 585(7823): 135-140.
[14] WU B, CHIEN E Y, MOL C D, et al. Structures of the CXCR4 chemokine GPCR with small-molecule and cyclic peptide antagonists [J]. Science, 2010, 330(6007): 1066-1071.
[15] TAN Q, ZHU Y, LI J, et al. Structure of the CCR5 chemokine receptor-HIV entry inhibitor maraviroc complex [J]. Science, 2013, 341(6152): 1387-1390.
[16] OSWALD C, RAPPAS M, KEAN J, et al. Intracellular allosteric antagonism of the CCR9 receptor [J]. Nature, 2016, 540(7633): 462-465.
[17] ZHENG Y, QIN L, ZACARIAS N V, et al. Structure of CC chemokine receptor 2 with orthosteric and allosteric antagonists [J]. Nature, 2016, 540(7633): 458-461.
[18] JAEGER K, BRUENLE S, WEINERT T, et al. Structural basis for allosteric ligand recognition in the human CC chemokine receptor 7 [J]. Cell, 2019, 178(5): 1222-1230. e10.
[19] KLEIST A B, GETSCHMAN A E, ZIAREK J J, et al. New paradigms in chemokine receptor signal transduction: moving beyond the two-site model [J]. Biochem Pharmacol, 2016, 114: 53- 68.
[20] SCHOLTEN D J, CANALS M, MAUSSANG D, et al. Pharmacological modulation of chemokine receptor function [J]. Br J Pharmacol, 2012, 165(6): 1617-1643.
[21] CRUMP M P, GONG J H, LOETSCHER P, et al. Solution structure and basis for functional activity of stromal cell-derived factor-1; dissociation of CXCR4 activation from binding and inhibition of HIV-1 [J]. EMBO J, 1997, 16(23): 6996-7007.
[22] PRADO G N, SUETOMI K, SHUMATE D, et al. Chemokine signaling specificity: Essential role for the N-terminal domain of chemokine receptors [J]. Biochemistry, 2007, 46(31): 8961-8968.
[23] ROUMEN L, SCHOLTEN D J, DE KRUIJF P, et al. C(X)CR in silico: Computer-aided prediction of chemokine receptor-ligand interactions [J]. Drug Discov Today Technol, 2012, 9(4): e281-291.
[24] KOEHL A, HU H, MAEDA S, et al. Structure of the micro-opioid receptor-Gi protein complex [J]. Nature, 2018, 558(7711): 547-552.
[25] GARCIA-NAFRIA J, NEHME R, EDWARDS P C, et al. Cryo-EM structure of the serotonin 5-HT1B receptor coupled to heterotrimeric Go [J]. Nature, 2018, 558(7711): 620-623.
[26] DRAPER-JOYCE C J, KHOSHOUEI M, THAL D M, et al. Structure of the adenosine-bound human adenosine A1 receptor-Gi complex [J]. Nature, 2018, 558(7711): 559-563.
[27] MAEDA S, QU Q, ROBERTSON M J, et al. Structures of the M1 and M2 muscarinic acetylcholine receptor/G-protein complexes [J]. Science, 2019, 364(6440): 552-557.
[28] HUA T, LI X, WU L, et al. Activation and signaling mechanism revealed by cannabinoid receptor-Gi complex structures [J]. Cell, 2020, 180(4): 655-665. e18.
[29] KRISHNA KUMAR K, SHALEV-BENAMI M, ROBERTSON M J, et al. Structure of a signaling cannabinoid receptor 1-G protein complex [J]. Cell, 2019, 176(3): 448-458. e12.
[30] XING C, ZHUANG Y, XU T H, et al. Cryo-EM Structure of the human cannabinoid receptor CB2-Gi signaling complex [J]. Cell, 2020, 180(4): 645-654. e13.
[31] RASMUSSEN S G F, DEVREE B T, ZOU Y, et al. Crystal structure of the β2 adrenergic receptor-Gs protein complex [J]. Nature, 2011, 477(7366): 549-555.
[32] MURPHY P M, TIFFANY H L. Cloning of complementary DNA encoding a functional human interleukin-8 receptor. Science. 1991. 253: 1280-1283 [J]. J Immunol, 2009, 183(5): 2898-2901.
[33] NASSER M W, RAGHUWANSHI S K, GRANT D J, et al. Differential activation and regulation of CXCR1 and CXCR2 by CXCL8 monomer and dimer [J]. J Immunol, 2009, 183(5): 3425- 3432.
/
| 〈 |
|
〉 |