

G蛋白偶联受体的共同激活机制
收稿日期: 2020-10-01
网络出版日期: 2021-02-25
Common activation mechanism of GPCR
Received date: 2020-10-01
Online published: 2021-02-25
周庆同, 戴之卓, 赵素文 . G蛋白偶联受体的共同激活机制[J]. 自然杂志, 2021 , 43(1) : 45 -52 . DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.0253-9608.2021.01.007
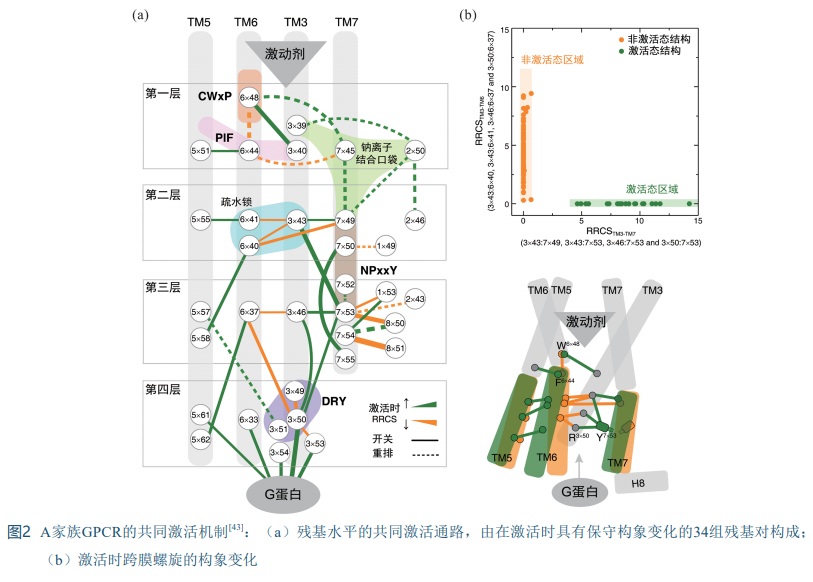
[1] VENKATAKRISHNAN A J, DEUPI X, LEBON G, et al. Molecular signatures of G-protein-coupled receptors [J]. Nature, 2013, 494(7436): 185-194.
[2] KATRITCH V, CHEREZOV V, STEVENS R C. Structure-function of the G protein-coupled receptor superfamily [J]. Annual Review of Pharmacology and Toxicology, 2013, 53: 531-556.
[3] HAUSER A S, CHAVALI S, MASUHO I, et al. Pharmacogenomics of GPCR drug targets [J]. Cell, 2018, 172(1/2): 41-54.
[4] HAUSER A S, ATTWOOD M M, RASK-ANDERSEN M, et al. Trends in GPCR drug discovery: new agents, targets and indications [J]. Nat Rev Drug Discov, 2017, 16 (12): 829-842.
[5] LEFKOWITZ R J. A brief history of G-protein coupled receptors (Nobel Lecture) [J]. Angew Chem Int Ed Engl, 2013, 52 (25), 6366- 6378.
[6] WEIS W I, KOBILKA B K. The molecular basis of G proteincoupled receptor activation [J]. Annual Review of Biochemistry, 2018, 87: 897-919.
[7] THAL D M, GLUKHOVA A, SEXTON P M, et al. Structural insights into G-protein-coupled receptor allostery [J]. Nature, 2018, 559(7712): 45-53.
[8] HUA T, VEMURI K, PU M, et al. Crystal structure of the human cannabinoid receptor CB1 [J]. Cell, 2016, 167 (3): 750-762.
[9] HUA T, LI X, WU L, et al. Activation and signaling mechanism revealed by cannabinoid receptor-Gi complex structures [J]. Cell, 2020, 180(4): 655-665.
[10] 张浩楠, 吴蓓丽. G蛋白偶联受体的结构生物学研究[J]. 自然杂 志,2016, 38(3): 193-199.
[11] ROSENBAUM D M, CHEREZOV V, HANSON M A, et al. GPCR engineering yields high-resolution structural insights into β2- adrenergic receptor function [J]. Science, 2007, 318(5854): 1266- 1273.
[12] RASMUSSEN S G, DEVREE B T, ZOU Y, et al. Crystal structure of the β2 adrenergic receptor-Gs protein complex [J]. Nature, 2011, 477(7366): 549-555.
[13] KANG Y, ZHOU X E, GAO X, et al. Crystal structure of rhodopsin bound to arrestin by femtosecond X-ray laser [J]. Nature, 2015, 523(7562): 561-567.
[14] ZHANG Y, SUN B, FENG D, et al. Cryo-EM structure of the activated GLP-1 receptor in complex with a G protein [J]. Nature, 2017, 546(7657): 248-253.
[15] GARCIA-NAFRIA J, TATE C G. Cryo-electron microscopy: moving beyond X-ray crystal structures for drug receptors and drug development [J]. Annual Review of Pharmacology and Toxicology, 2020, 60: 51-71.
[16] ZHANG H, QIAO A, YANG D, et al. Structure of the full-length glucagon class B G-protein-coupled receptor [J]. Nature, 2017, 546(7657): 259-264.
[17] SONG G, YANG D, WANG Y, et al. Human GLP-1 receptor transmembrane domain structure in complex with allosteric modulators [J]. Nature, 2017, 546(7657): 312-315.
[18] ZHAO L H, MA S, SUTKEVICIUTE I, et al. Structure and dynamics of the active human parathyroid hormone receptor-1 [J]. Science, 2019, 364(6436): 148-153.
[19] HUA T, VEMURI K, NIKAS S P, et al. Crystal structures of agonist-bound human cannabinoid receptor CB1 [J]. Nature, 2017, 547(7664): 468-471.
[20] MAO C, SHEN C, LI C, et al. Cryo-EM structures of inactive and active GABAB receptor [J]. Cell Res, 2020, 30(7): 564-573. [21] YANG F, MAO C, GUO L, et al. Structural basis of GPBAR activation and bile acid recognition [J]. Nature, 2020, 587: 499-504.
[22] YANG S F, WU Y R, XU T H, et al. Crystal structure of the Frizzled 4 receptor in a ligand-free state [J]. Nature, 2018, 560(7720): 666- 670.
[23] LIU K, WU L, YUAN S, et al. Structural basis of CXC chemokine receptor 2 activation and signalling [J]. Nature, 2020, 585(7823): 135-140.
[24] YU J, GIMENEZ L E, HERNANDEZ C C, et al. Determination of the melanocortin-4 receptor structure identifies Ca(2+) as a cofactor for ligand binding [J]. Science, 2020, 368(6489): 428-433.
[25] LIN X, LI M, WANG N, et al. Structural basis of ligand recognition and self-activation of orphan GPR52 [J]. Nature, 2020, 579(7797): 152-157.
[26] PENG Y, MCCORVY J D, HARPSOE K, et al. 5-HT2C receptor structures reveal the structural basis of GPCR polypharmacology [J]. Cell, 2018, 172(4): 719-730.
[27] EDDY M T, LEE M Y, GAO Z G, et al. Allosteric coupling of drug binding and intracellular signaling in the A2A adenosine receptor [J]. Cell, 2018, 172(1/2): 68-80.
[28] LIU J J, HORST R, KATRITCH V, et al. Biased signaling pathways in β2-adrenergic receptor characterized by 19F-NMR [J]. Science, 2012, 335(6072): 1106-1110.
[29] SUSAC L, EDDY M T, DIDENKO T, et al. A2A adenosine receptor functional states characterized by (19)F-NMR [J]. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA, 2018, 115(50): 12733-12738.
[30] YE L, VAN EPS N, ZIMMER M, et al. Activation of the A2A adenosine G-protein-coupled receptor by conformational selection [J]. Nature, 2016, 533(7602): 265-268.
[31] NYGAARD R, ZOU Y, DROR R O, et al. The dynamic process of β2-adrenergic receptor activation [J]. Cell, 2013, 152(3): 532-542.
[32] LATORRACA N R, VENKATAKRISHNAN A J, DROR R O. GPCR dynamics: structures in motion [J]. Chem Rev, 2017, 117(1): 139-155.
[33] SUOMIVUORI C M, LATORRACA N R, WINGLER L M, et al. Molecular mechanism of biased signaling in a prototypical G protein-coupled receptor [J]. Science, 2020, 367(6480): 881-887.
[34] VENKATAKRISHNAN A J, DEUPI X, LEBON G, et al. Diverse activation pathways in class A GPCRs converge near the G-proteincoupling region [J]. Nature, 2016, 536(7617): 484-487.
[35] PANDY-SZEKERES G, MUNK C, TSONKOV T M, et al. GPCRdb in 2018: adding GPCR structure models and ligands [J]. Nucleic Acids Res, 2018, 46: 440-446.
[36] TRZASKOWSKI B, LATEK D, YUAN S, et al. Action of molecular switches in GPCRs—theoretical and experimental studies [J]. Curr Med Chem, 2012, 19(8): 1090-1109.
[37] ISHCHENKO A, WACKER D, KAPOOR M, et al. Structural insights into the extracellular recognition of the human serotonin 2B receptor by an antibody [J]. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA, 2017, 114(31): 8223-8228.
[38] SCHONEGGE A M, GALLION J, PICARD L P, et al. Evolutionary action and structural basis of the allosteric switch controlling β2AR functional selectivity [J]. Nat Commun, 2017, 8(1): 2169.
[39] ALHADEFF R, VOROBYOV I, YOON H W, et al. Exploring the free-energy landscape of GPCR activation [J]. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA, 2018, 115(41): 10327-10332.
[40] ROTH B L, IRWIN J J, SHOICHET B K. Discovery of new GPCR ligands to illuminate new biology [J]. Nat Chem Biol, 2017, 13(11): 1143-1151.
[41] KATRITCH V, FENALTI G, ABOLA E E, et al. Allosteric sodium in class A GPCR signaling [J]. Trends Biochem Sci, 2014, 39(5): 233-244.
[42] NGO T, ILATOVSKIY A V, STEWART A G, et al. Orphan receptor ligand discovery by pickpocketing pharmacological neighbors [J]. Nat Chem Biol, 2017, 13(2): 235-242.
[43] ZHOU Q, YANG D, WU M, et al. Common activation mechanism of class A GPCRs [J]. eLife, 2019, 8: 50279.
[44] THOMPSON M D, HENDY G N, PERCY M E, et al. G proteincoupled receptor mutations and human genetic disease [J]. Methods Mol Biol, 2014, 1175: 153-187.
[45] ERDELYI L S, MANN W A, MORRIS-ROSENDAHL D J, et al. Mutation in the V2 vasopressin receptor gene, AVPR2, causes nephrogenic syndrome of inappropriate diuresis [J]. Kidney Int, 2015, 88(5): 1070-1078.
[46] PASEL K, SCHULZ A, TIMMERMANN K, et al. Functional characterization of the molecular defects causing nephrogenic diabetes insipidus in eight families [J]. J Clin Endocrinol Metab, 2000, 85(4): 1703-1710.
/
| 〈 |
|
〉 |