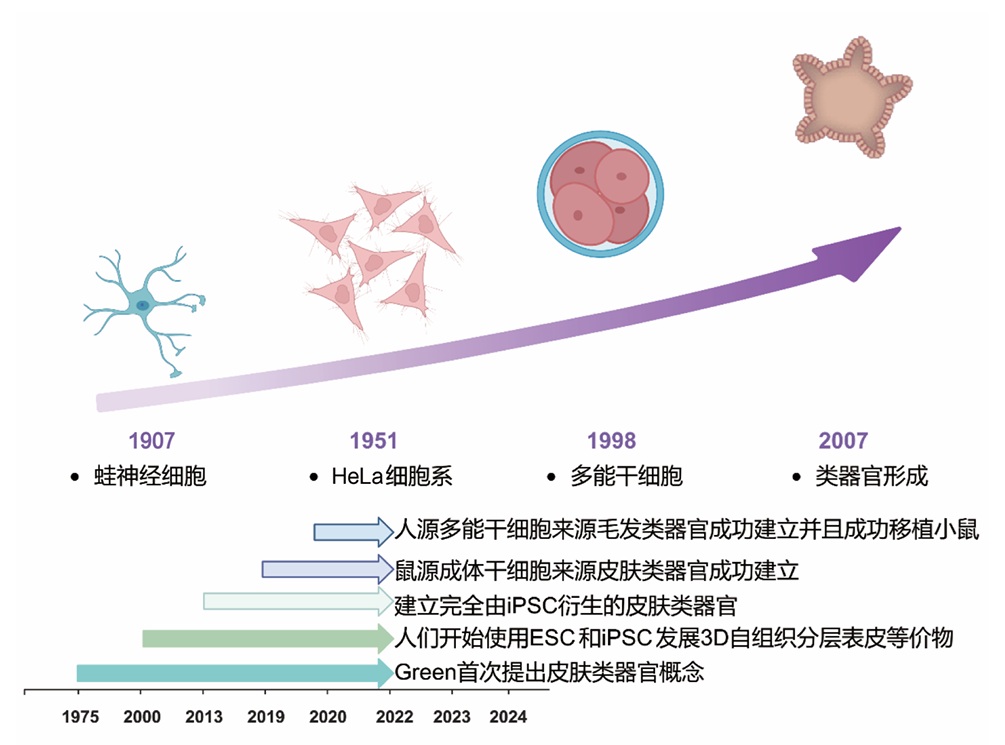
皮肤是人体最大的器官,由表皮和真皮紧密相邻组成。皮肤在人类生命中发挥着许多重要作用,例如屏障、体温调节、感觉和免疫等。近年来,随着类器官研究的蓬勃发展,皮肤类器官越来越受到关注,并得到广泛的应用。本文总结了复合型皮肤类器官和单独皮肤附属物类器官,从iPSC诱导分化到成体干细胞自组装成类器官的不同构建方法、培养条件,归纳
了皮肤类器官的不同应用场景,包括疾病模型、组织器官再生、肿瘤研究、药效评价等,并在已有研究成果的基础上,给出皮肤类器官技术未来发展的建议,以期为皮肤类器官的更深入研究提供合理的参考。
Skin, the largest organ of the human body, is composed of closely adjacent epidermis and dermis, which plays vital roles
in human life, including barrier function, thermoregulation, sensation, and immunity. In recent years, with the rapid advancement
of organoid research, skin organoids have garnered increasing attentions and have been widely applied. This review systematically
summarizes current methodologies for constructing both composite skin organoids and individual skin appendage organoids,
encompassing differentiation induction from induced pluripotent stem cells (iPSCs) to self-organization of adult stem cells into
organoids. Additionally, it outlines the diverse applications of skin organoids, such as disease modeling, regeneration of tissues and
organs, tumor research, and drug efficacy evaluation. In addition to comprehensively evaluating existing constraints in skin organoid
development, we present targeted recommendations for technological innovation, establishing a conceptual foundation for advancing
this field.